Sanddorn
- Scarlet Allen
- Jan 14
- 3 min read
Hippophae rhamnoides
The sea buckthorn, also known as the "lemon of the north", belongs to the oleaster family (Elaeagnaceae). With its bright orange fruits, it is not only an eye-catcher, but also a valuable medicinal and useful plant that is characterized by its robustness and versatility. The fruits are known for their high vitamin C content and are processed in particular into food and drinks as well as skin care products.

Appearance and habitat
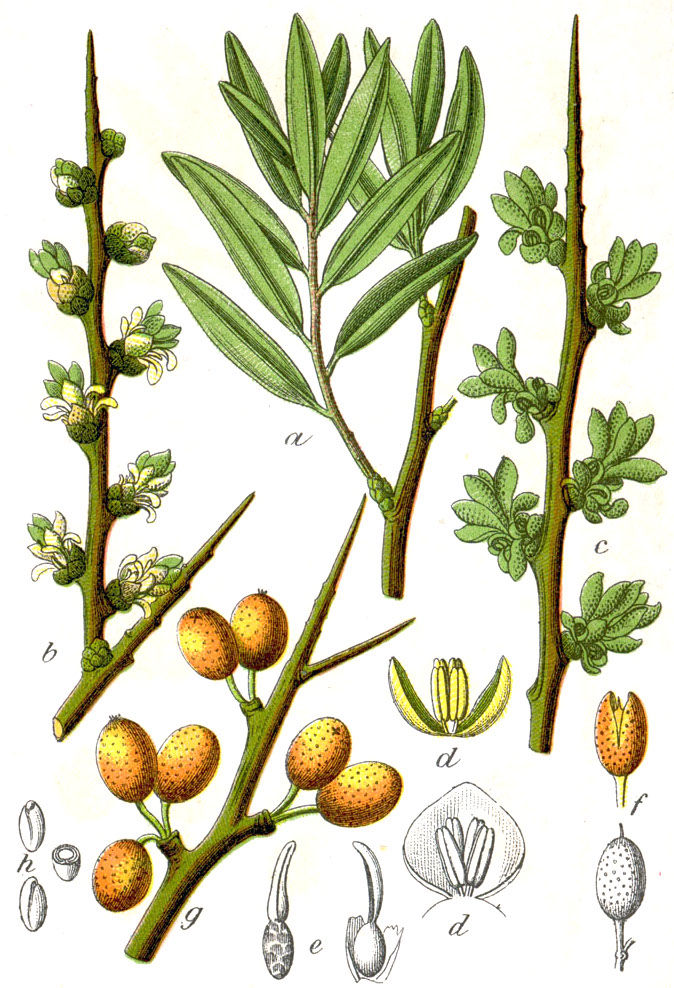
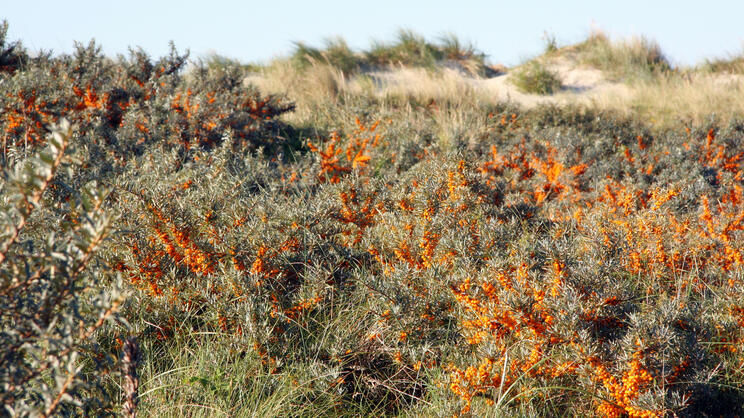
The sea buckthorn is a thorny, summer green shrub that reaches heights of up to 5 meters. Its narrow, silvery-green leaves and dense branches make it wind and weather resistant. Sea buckthorn prefers to grow in sandy, nutrient-poor soils and is native mainly to coastal and river regions in Europe and Asia. It is a pioneer tree that also thrives in barren locations and is used to stabilize the soil. Sea buckthorn is salt-resistant, which allows the shrub to thrive even on nasty coasts. Hence the name.
history
Sea buckthorn is widespread in large parts of Europe and Asia and is particularly valued in coastal regions and the Himalayas. Its use goes back a long way: it was already known for its medicinal properties in ancient times. In the Middle Ages, sea buckthorn berries were used to strengthen and heal wounds, and even today it is highly valued in traditional and modern medicine.
Habitat: coastal, pioneer plant, full sun
Distribution area: Asia, Europe
Flower: yellow, inconspicuous
Main flowering period: March-May
Harvest time: from August
Growth: bushy, up to 5 meters high
Edible parts: fruits, seeds
Other uses: cosmetics, medicine, nitrogen fixer
Plants found in Son Selva: 5
edible Uses
The bright orange sea buckthorn berries are extremely rich in vitamin C - their content exceeds that of lemons many times over - and also contain antioxidants, beta-carotene and omega-3 fatty acids. The berries taste very sour on their own and are therefore usually processed into juices, jams, syrups or liqueurs, which means they lose vitamin C.

Other uses
Medicinal plant: Sea buckthorn oil, which is extracted from the fruits and seeds, is used in naturopathy to care for the skin and mucous membranes, as well as for gastrointestinal complaints.
Cosmetics: Sea buckthorn oil is a popular ingredient in creams and ointments because it regenerates and protects the skin.
Soil protection: The deep-rooted sea buckthorn protects soils from erosion and improves their structure.
Nitrogen fixation: The roots of the sea buckthorn form a symbiosis with nitrogen-fixing actinobacteria, which bind the nitrogen contained in the air and make it available to the plant. In this way, the sea buckthorn improves soil fertility and creates optimal conditions for the growth of neighboring plants.
In addition, it serves as a windbreak and erosion protection, especially on sandy or barren soils. Its deep roots stabilize the subsoil, while the dense branches and leaves provide protection for smaller plants. The thorny branches also make it an effective habitat for birds and insects, which play an important role in permaculture systems.

Planting
Sea buckthorn needs a lot of light and the soil should be deep and not too acidic. Heavy clay soils in particular must be loosened with plenty of sand, because sea buckthorn does not grow on soils with little air. Sea buckthorn is superior to all other woody plants, particularly along the coast, due to its wind resistance and salt tolerance.
Sea buckthorn is dioecious, which means that the fruits only form on the female plants. For reliable yields, at least one male specimen must be planted as a pollen donor for up to five female bushes. Since the flowers are pollinated by wind, the male plant should be planted taking the main wind direction into account.
If sea buckthorn is allowed to grow freely, the crown will become wider over time. The fruits only form in the outer crown area, while the interior of the crown becomes increasingly bare and woody. To counteract this, the harvested shoots are cut back to short shoots every two years in late winter and the bushes are thinned out a little if necessary. Tip: Plant at least two female and one male bush, because sea buckthorn only produces a good yield every two years. If the two female bushes are cut back alternately every winter, they can be harvested every year.




Comentarios